One of the worlds most deadly virus known as Ebola has claimed hundreds of life in its recent outbreak in west Africa.
The Ebola Virus Disease(EVD) has brought fear and panic in our world killing over 2000 people in west Africa.
Ebola was first discovered in Guinea spreading through Sierra Leone, Liberia and now in Nigeria.
Ebola is a highly infectious disease killing up to 90% of the people who catch it causing fear and terror among infected communities as there is no known vaccine for it.
Here are what you should know about EVD
WHAT IS EBOLA:
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) refer to Ebola to a group of virus that causes viral hemorrhagic fever causing multiple organ failure accompanied by internal and external bleeding.
The virus is named after the Ebola river in the democratic Republic of Congo(formally Zaire)
TYPES OF EBOLA:
There are five different strains of the virus according to the World Health Organization- Named after the area they originated in.
These are:
The Bundigyo Ebola- An area in Uganda where the virus was first discovered in 2007
Sudan Ebola
Zaire Ebola
The Ivory Coast Ebola- Discovered when a researcher studying wild chimpanzees became ill in 1994 after an autopsy of one of the animals. The researcher recovered.
Reston Ebola- Named after Reston in the US state of Virginia where its strain was discovered in monkeys imported from the Philippines.
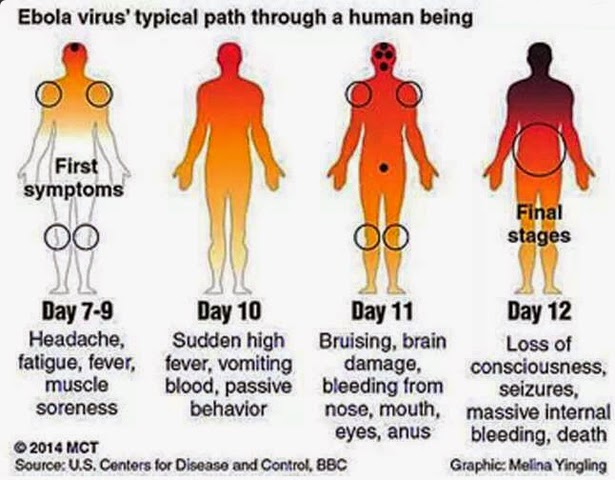
SYMPTOMS
Early symptoms include sudden onset fever, weakness, muscle pain, headaches and sore throat.
The early symptoms progress to vomiting, diarrhea, impaired kidney and liver function and some times internal and external bleeding.
TREATMENT
There are no known vaccine for Ebola.
Patients can only be isolated and then supported by health care workers.
This consists of hydrating the patient, maintaining their oxygen status and blood pressure and treating them for any complicating infections says MSF.
MODE OF SPREADING
It is believed that fruit bats may be the natural host for the Ebola virus in Africa passing it to other animals.
Human contract Ebola through contact with bodily fluid of infected animals and humans.
MSF says while the virus is believed to be able to survive for some days in liquid outside an infected organism, chlorine disinfectant, heat, direct sunlight, soaps and detergents can kill it.
NOTE: "The virus is not air borne", said Dr Marty Cetron, director of CDC's Division of Global Migration and Quarantine. "there need to be direct contact with bodily fluids or blood"








.jpg)




0 comments:
Post a Comment